1. Introduction
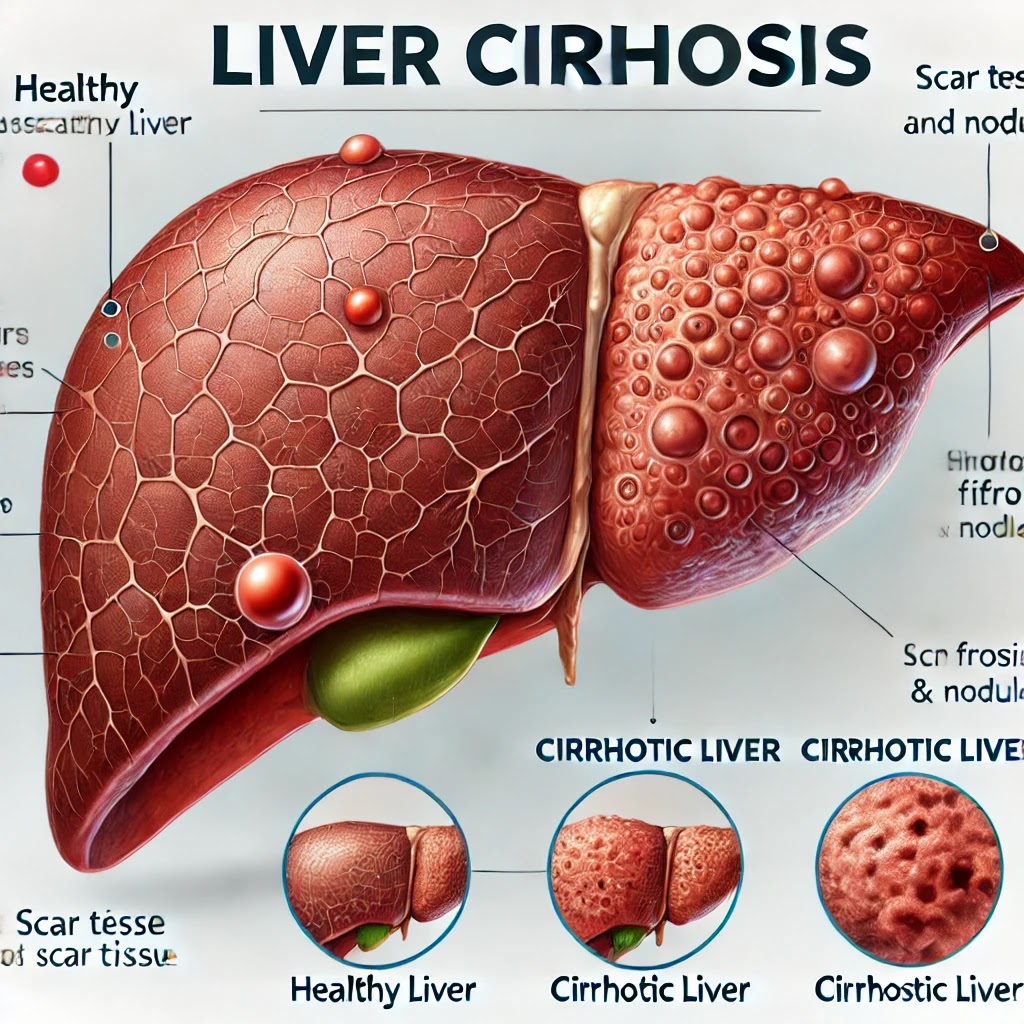
What is Liver Cirrhosis?
Liver cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease characterized by the replacement of healthy liver tissue with scar tissue, leading to a progressive decline in liver function. This scarring disrupts the normal structure and regenerative capabilities of the liver, which is crucial for processes like detoxification, protein synthesis, and the production of biochemicals necessary for digestion.
Importance of Understanding Liver Cirrhosis
Understanding liver cirrhosis is essential as it can significantly impact quality of life and can be fatal if not managed properly. Early detection and management can slow the progression of the disease, improve life expectancy, and reduce complications.
2. Causes of Liver Cirrhosis
Chronic Alcohol Abuse
One of the most common causes of liver cirrhosis is chronic alcohol abuse. Long-term alcohol consumption leads to repeated liver inflammation, eventually causing permanent scarring.
Hepatitis Infections
Chronic hepatitis B and C infections are major contributors to liver cirrhosis worldwide. These viral infections cause long-term liver inflammation, leading to damage and scarring over time.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD, associated with obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol, leads to fat buildup in the liver, which can progress to inflammation and cirrhosis if not managed effectively.
Other Contributing Factors
Other causes include autoimmune hepatitis, genetic disorders like hemochromatosis and Wilson’s disease, and prolonged exposure to toxins or certain medications.
3. Symptoms and Diagnosis
Early Symptoms
Early symptoms of liver cirrhosis can be subtle and are often overlooked. They may include fatigue, weakness, and mild abdominal pain.
Advanced Symptoms
As the disease progresses, symptoms become more pronounced and may include jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes), severe itching, easy bruising or bleeding, and swelling in the legs and abdomen.
Diagnostic Tests
Diagnosis typically involves blood tests to check liver function, imaging tests such as ultrasound or MRI to assess liver damage, and sometimes a liver biopsy to confirm cirrhosis.
4. Stages of Liver Cirrhosis
Compensated Cirrhosis
In this stage, the liver is scarred but still functions well. Many individuals may not experience any significant symptoms during this phase.
Decompensated Cirrhosis
This stage occurs when the liver can no longer perform its essential functions. Symptoms and complications become more severe, and medical intervention is often necessary.
End-Stage Liver Disease
This is the most severe form of cirrhosis, where the liver fails completely. Liver transplantation may be the only viable treatment option at this stage.
5. Complications of Liver Cirrhosis
Portal Hypertension
Scarring of the liver can lead to increased pressure in the portal vein, causing complications like varices, which can rupture and lead to life-threatening bleeding.
Ascites
Fluid accumulation in the abdomen, known as ascites, is a common complication. It can cause discomfort and difficulty breathing and often requires medical intervention.
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Toxin buildup due to reduced liver function can affect the brain, leading to confusion, mood changes, and impaired cognitive function.
Liver Cancer
Individuals with cirrhosis are at increased risk of developing liver cancer, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma, necessitating regular screening and monitoring.
6. Treatment Options
Lifestyle Modifications
Patients are advised to quit alcohol, manage weight, and control any underlying conditions such as diabetes or hypertension to slow disease progression.
Medications
Medications may be prescribed to manage symptoms and complications, such as diuretics for ascites, beta-blockers for portal hypertension, and lactulose for hepatic encephalopathy.
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions like a shunt placement or variceal banding may be required to manage complications.
Liver Transplantation
For end-stage liver disease, liver transplantation remains the only curative option, providing a new, healthy liver to replace the damaged one.
7. Diet and Nutrition
Foods to Avoid
Patients with liver cirrhosis should avoid alcohol, high-sodium foods, and foods high in unhealthy fats, which can exacerbate liver damage.
Recommended Foods
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains supports liver health and overall well-being.
Supplements and Vitamins
Supplements such as vitamin D and certain antioxidants may be recommended, but it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.
8. Prevention of Liver Cirrhosis
Reducing Alcohol Consumption
Limiting alcohol intake or abstaining altogether is a key preventive measure against cirrhosis.
Vaccination and Safe Practices for Hepatitis
Vaccinations against hepatitis B and practicing safe hygiene and safe sex can significantly reduce the risk of viral hepatitis, a major cause of cirrhosis.
Managing Underlying Conditions
Proper management of conditions such as obesity, diabetes, and high cholesterol can prevent the development of NAFLD and subsequent cirrhosis.
9. Living with Liver Cirrhosis
Monitoring and Regular Check-ups
Regular monitoring through blood tests, imaging, and consultations with healthcare providers is crucial for managing liver cirrhosis effectively.
Coping Strategies
Mental health support, stress management techniques, and joining support groups can provide emotional and psychological relief.
Support Systems
Building a strong support network of family, friends, and healthcare providers can help patients navigate the challenges of living with cirrhosis.
10. Expert Insights
Quotes from Hepatologists
Experts emphasize the importance of early detection and lifestyle changes in managing cirrhosis. “Early intervention can significantly alter the disease course,” says Dr. Jane Smith, a leading hepatologist.
Patient Case Studies
Case studies highlight how patients who adopted lifestyle changes and adhered to medical advice experienced slower disease progression and improved quality of life.
11. Future Outlook
Advances in Treatment
Ongoing research is exploring new medications, regenerative therapies, and less invasive surgical options to treat cirrhosis more effectively.
Potential Cures and Research
While liver transplantation is currently the only cure, advances in gene therapy and stem cell research offer hope for future treatments that could regenerate damaged liver tissue.
12. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Can liver cirrhosis be reversed?
- In its early stages, lifestyle changes can halt or partially reverse damage, but in advanced stages, the scarring is usually permanent.
- Is cirrhosis always caused by alcohol?
- No, cirrhosis can be caused by viral hepatitis, NAFLD, genetic disorders, and other factors unrelated to alcohol consumption.
- What are the chances of survival with cirrhosis?
- Survival rates depend on the stage of cirrhosis, overall health, and treatment adherence. Early-stage cirrhosis has a better prognosis.
13. Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Liver cirrhosis is a serious, often preventable condition that significantly impacts health and quality of life. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and treatment options is crucial for early intervention and management.
Encouragement for Prevention and Early Detection
By adopting healthy lifestyle habits and seeking regular medical care, individuals can reduce their risk of developing liver cirrhosis and improve outcomes if diagnosed.